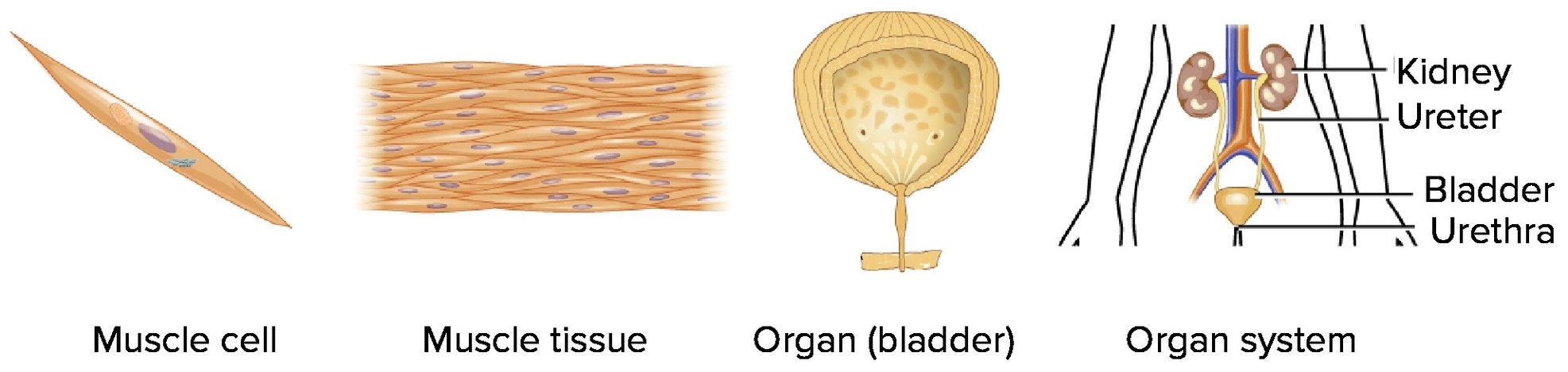
Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems
Cells are the smallest unit of life. They come in various shapes and serve specialized purposes in the body. For instance, muscle cells contract, nerve cells transmit impulses, red blood cells bind to oxygen, and white blood cells fight infection.
When cells of a certain type group together, the resulting structure is called tissue. There are various types of tissues, including muscle tissue (made of strands of muscle cells), adipose tissue (comprised of fat cells), and connective tissue (various types of tough, fibrous matter like tendons or ligaments).
Organs are structures made up of two or more tissues organized to carry out a particular function. For example, the heart, an organ, has muscle tissue, connective tissue, and nerve tissue all working together to pump blood. Organs can perform more than one function, and each function can be quite complicated.
Organ systems are groups of organs that work together, carrying out processes that keep us alive. For example, your digestive system is responsible for taking in and processing food, while your respiratory systemworking with your circulatory systemis responsible for taking up oxygen and getting rid of carbon dioxide. The muscular and skeletal systems are crucial for movement; the reproductive system handles reproduction; and the excretory system gets rid of metabolic waste. These different systems are dependent on each other.
The rise of the Western concept of nationalism disrupted the Ottoman Empire’s traditional millet system. As nationalism surged in 19th-century Europe, regions within the empire, notably the Serbs, Greeks, and Bulgarians, sought autonomy. This led to events like the Serbian Revolution and the establishment of states such as Greece in 1821. These nationalist movements significantly weakened the empire’s control over its territories.
The organization of the human body starts with these building blocks: cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. Whether you’re talking about the delicate tissue of the brain or the hardness of bone, it’s still made of cells banded together into tissue and organized into organs.