The human brain, a complex organ, is the control center for the body’s functions and the seat of human consciousness. It processes, integrates, and coordinates information received from the sense organs, and makes decisions as to the instructions sent to the rest of the body.
Composition
Weighing about 3 pounds in the average adult, the brain is about 60% fat. The remaining 40% is a combination of water, protein, carbohydrates, and salts. It contains blood vessels and nerves, including neurons and glial cells.
Gray Matter and White Matter
Gray and white matter are two different regions of the central nervous system. In the brain, gray matter refers to the darker, outer portion, while white matter describes the lighter, inner section underneath. Gray matter is primarily composed of neuron somas (the round central cell bodies), and white matter is mostly made of axons (the long stems that connect neurons together) wrapped in myelin (a protective coating). Gray matter is primarily responsible for processing and interpreting information, while white matter transmits that information to other parts of the nervous system.
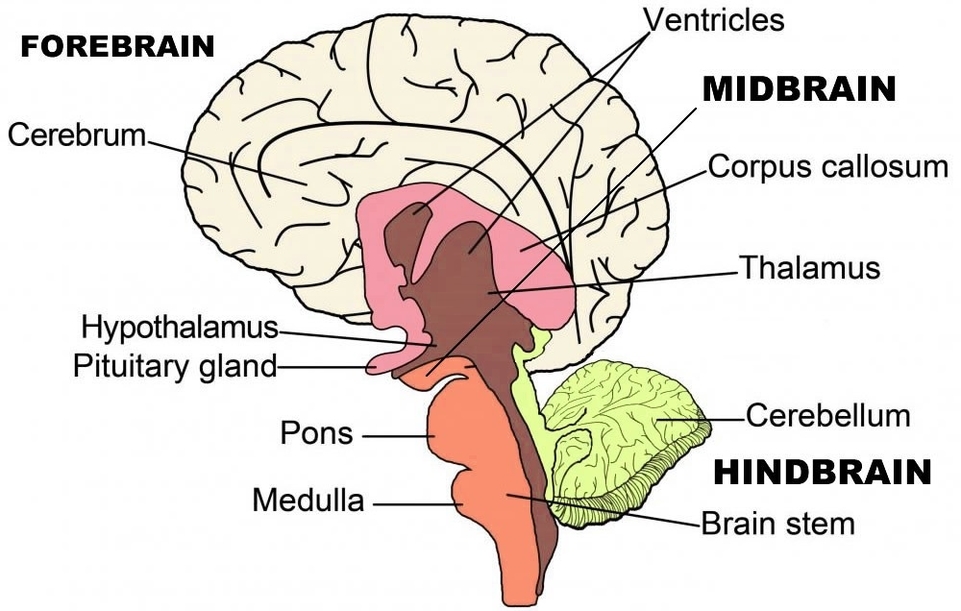
Main Parts of the Brain and Their Functions
At a high level, the brain can be divided into the cerebrum, brainstem, and cerebellum.
1. Cerebrum: The cerebrum (front of brain) comprises gray matter (the cerebral cortex) and white matter at its center. The largest part of the brain, the cerebrum initiates and coordinates movement and regulates temperature. Other areas of the cerebrum enable speech, judgment, thinking and reasoning, problem-solving, emotions and learning. Other functions relate to vision, hearing, touch, and other senses.
2. Cerebral Cortex: The cortex has a large surface area due to its folds, and comprises about half of the brains weight. The cerebral cortex is divided into two halves, or hemispheres. It is covered with ridges (gyri) and folds (sulci).
3. Brainstem: The brainstem connects the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord, performing many automatic functions such as breathing, heart rate, body temperature, wake and sleep cycles, digestion, sneezing, and coughing.
4. Cerebellum: The cerebellum is located under the cerebrum. Its function is to coordinate muscle movements, maintain posture, and balance.
Brain Function
The brain sends and receives chemical and electrical signals throughout the body. Different signals control different processes, and your brain interprets each. Some make you feel tired, for example, while others make you feel pain. Some messages are kept within the brain, while others are relayed through the spine and across the bodys vast network of nerves to distant extremities.
In conclusion, the brain is a marvel of nature, a complex organ that not only controls the numerous physical functions of the body but also houses the essence of the individual. Its structure and function are the subjects of ongoing scientific exploration, and its mysteries continue to offer vast fields for future discovery..