An anatomy image of accessory organs emphasizes structures that support major systems without forming the main pathway. Common examples include the liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and salivary glands. The layout shows how these organs connect to primary organs like the digestive tract, supplying enzymes, bile, or hormones that aid digestion and metabolism. Rather than transporting food directly, these organs modify, regulate, or store substances needed for normal function. Labels often point out ducts, secretory regions, and relationships to nearby organs. Seeing these structures together helps explain why damage to an accessory organ can disrupt an entire system, even though food or blood never directly passes through them.
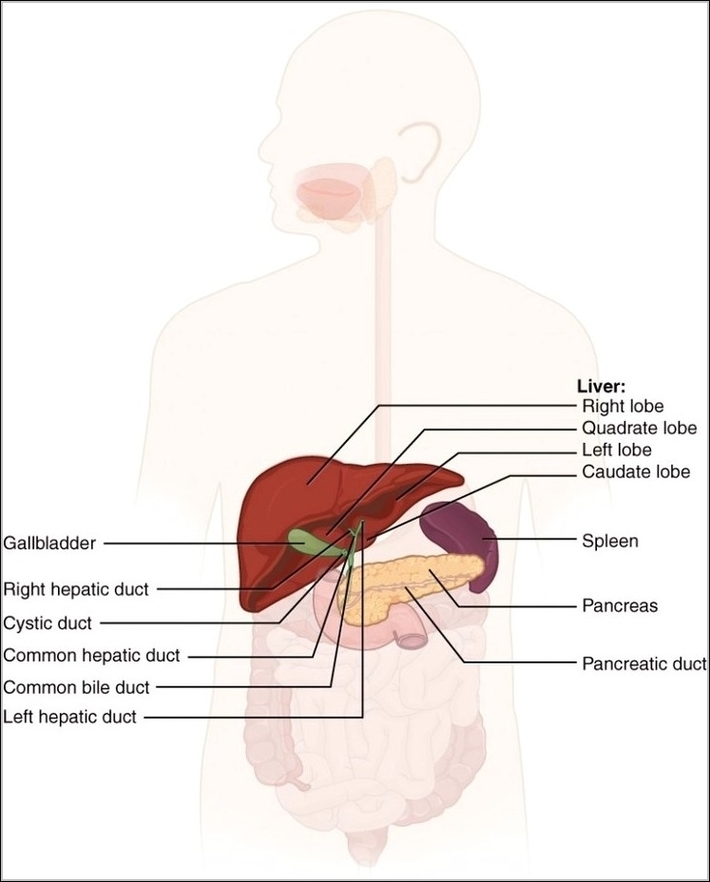
Accessory Organs
Posted inOrgans