Posted inDiagrams
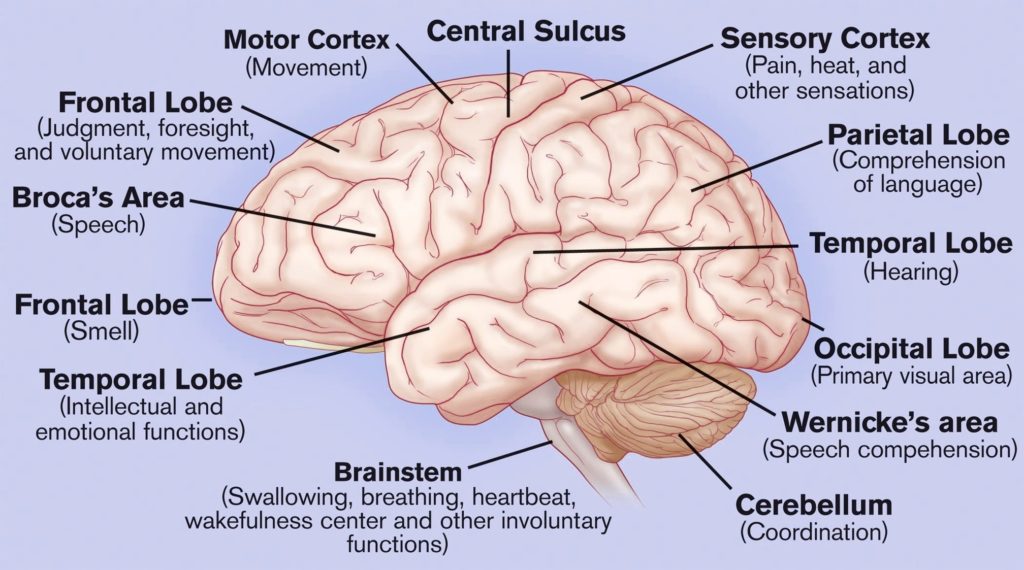
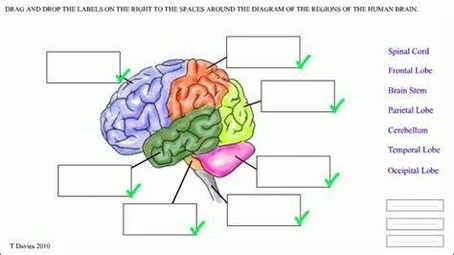
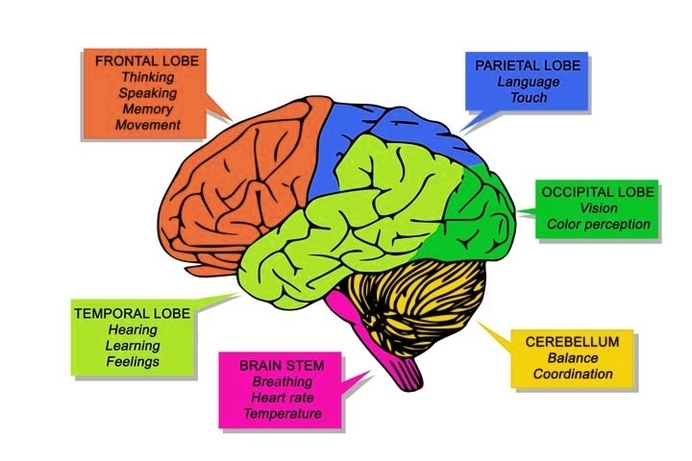
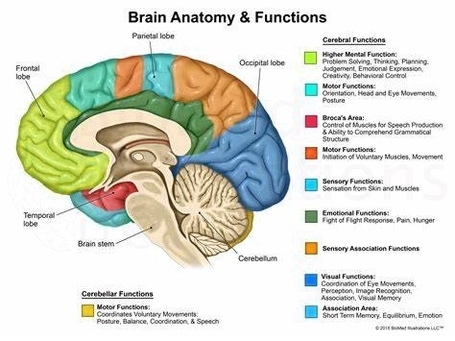
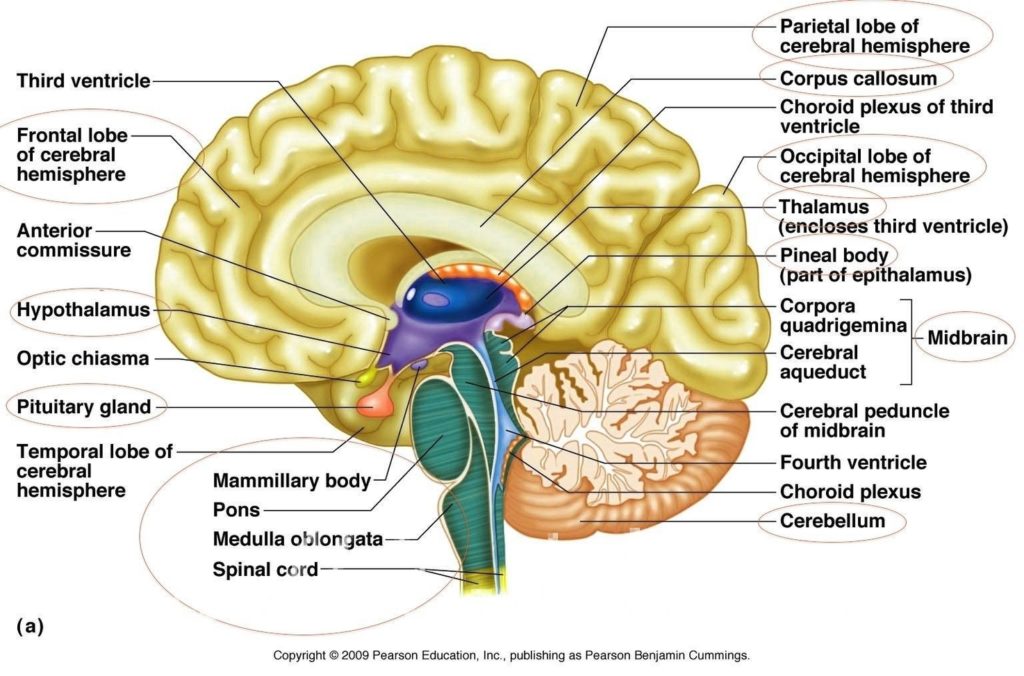
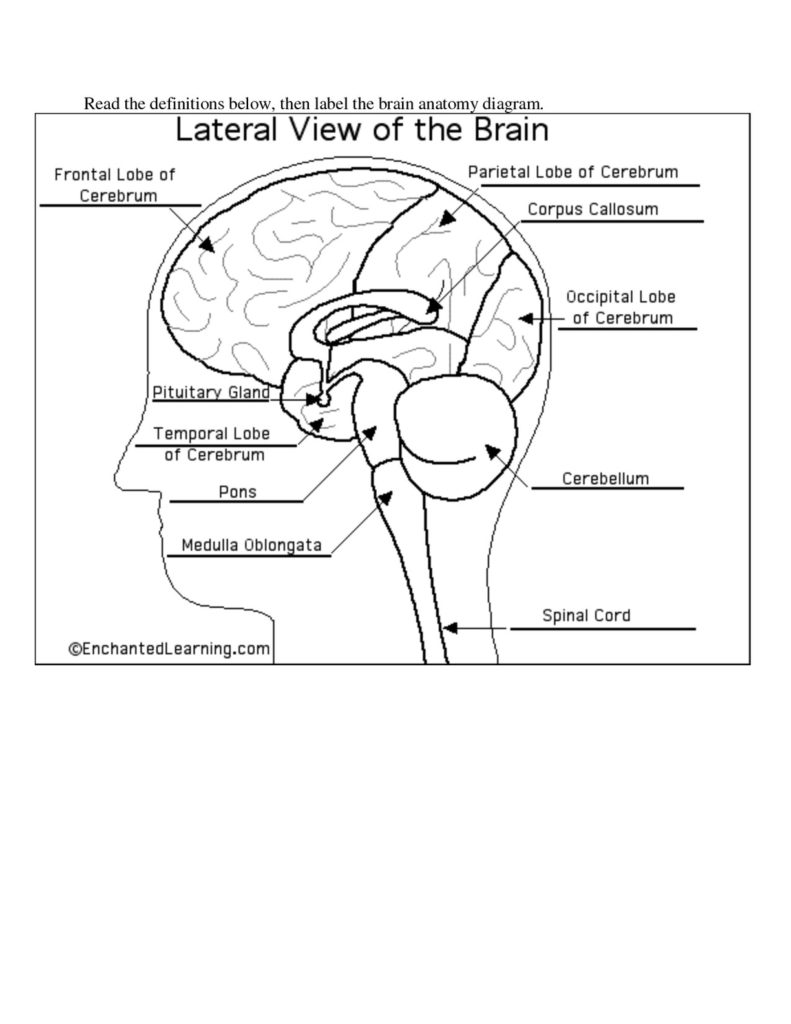
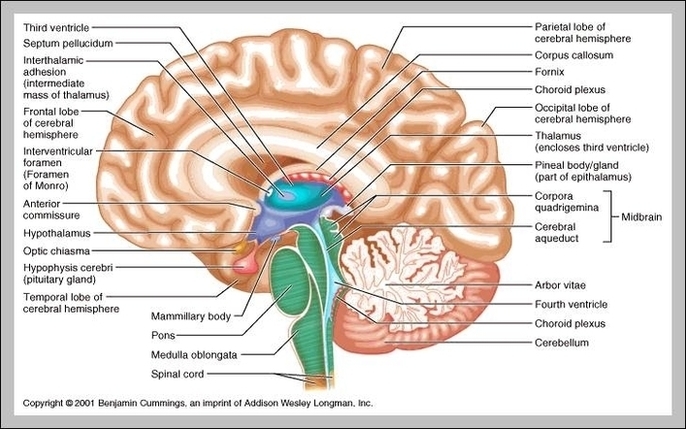
Basic Structure Of The Human Brain
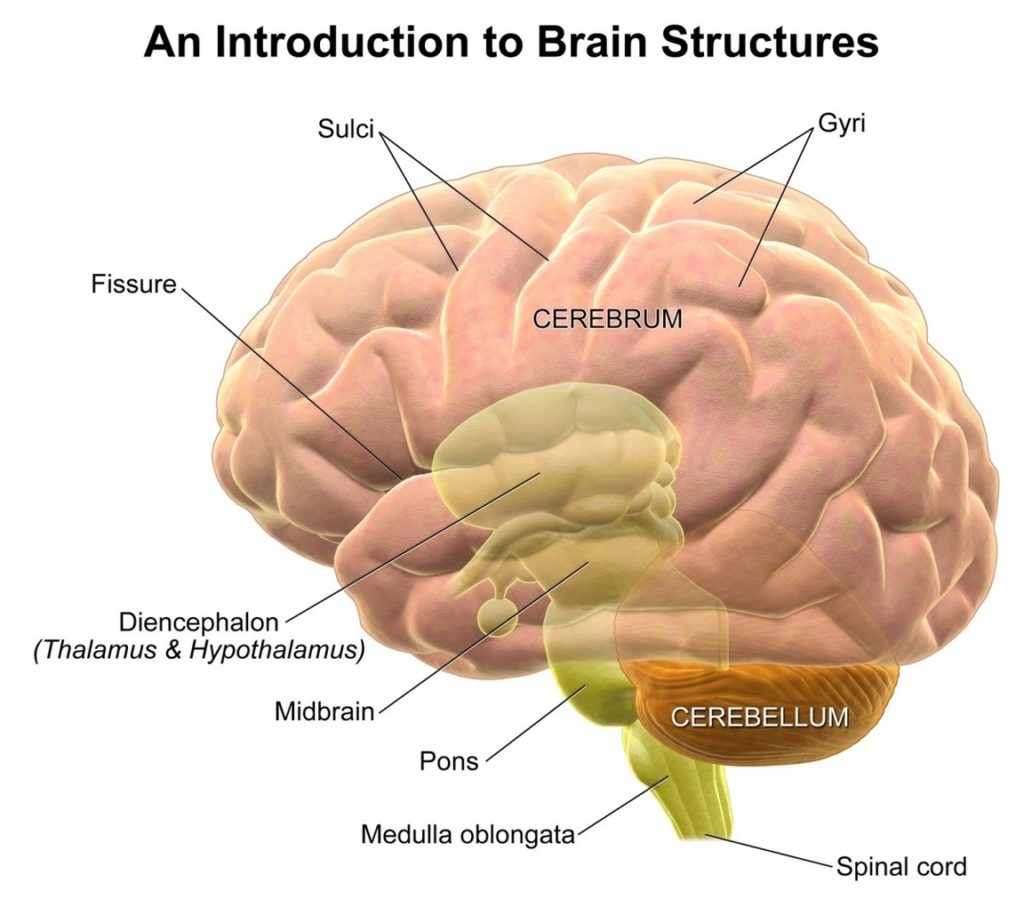
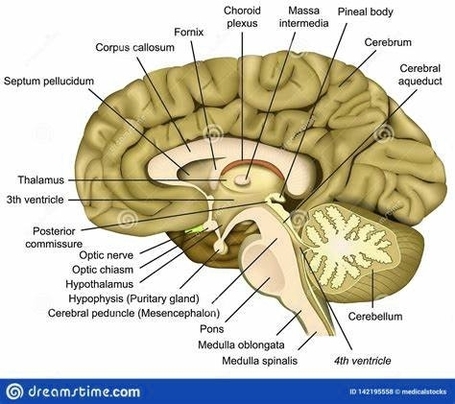
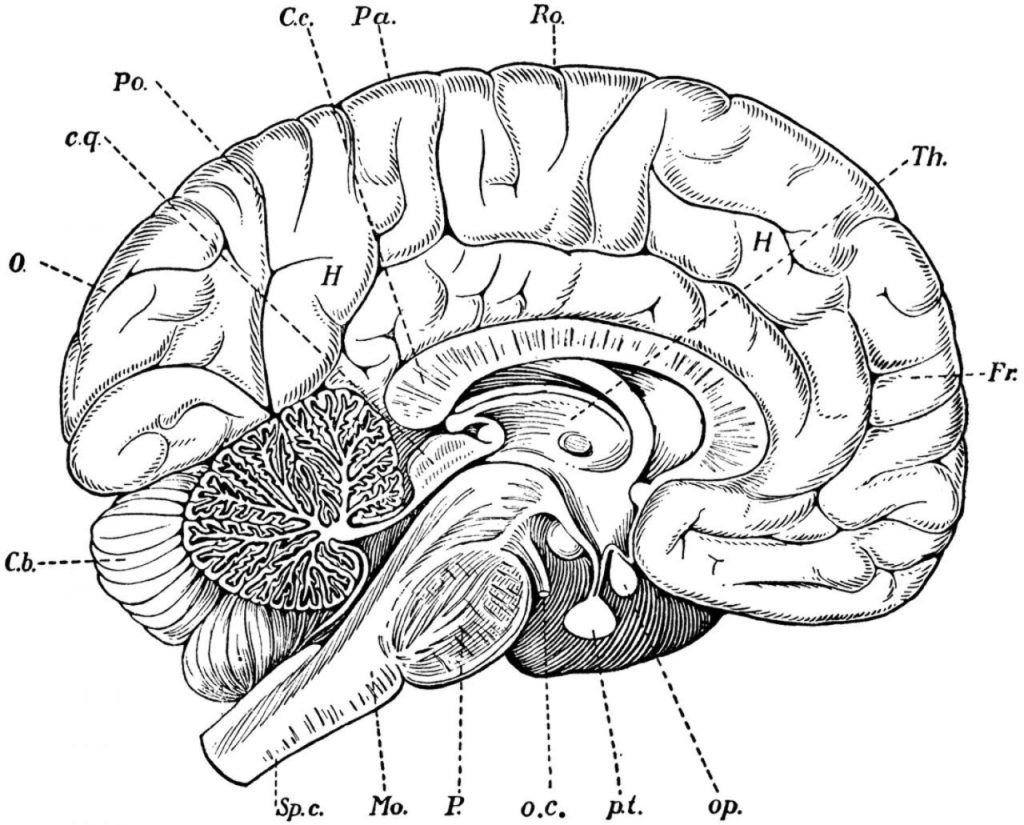
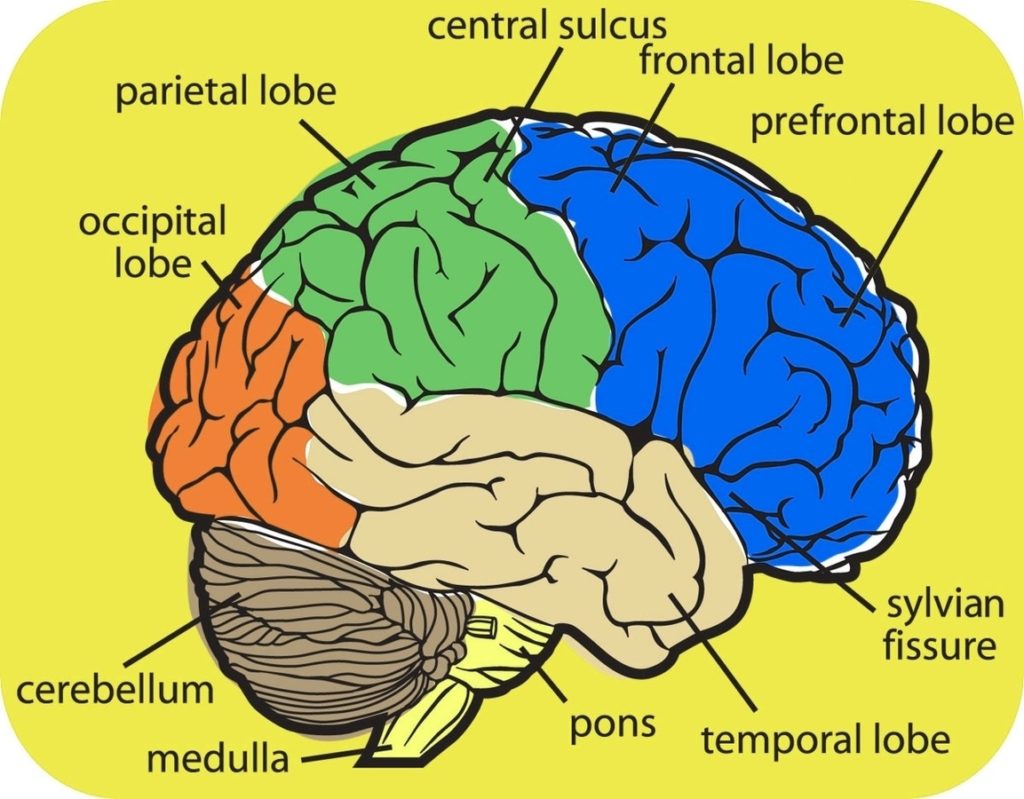
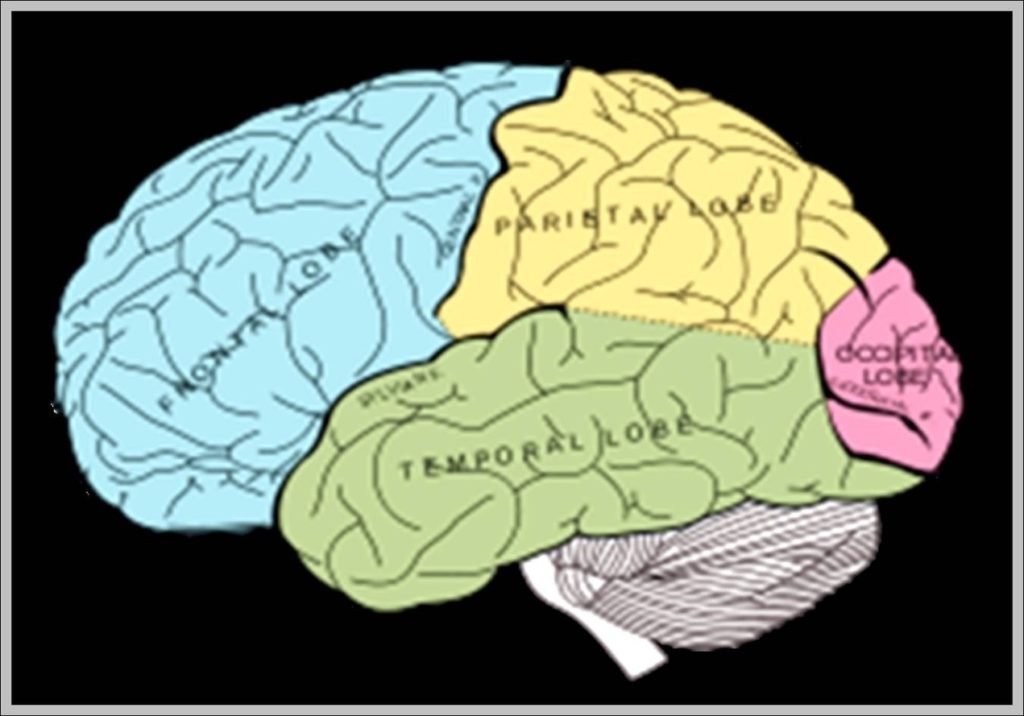
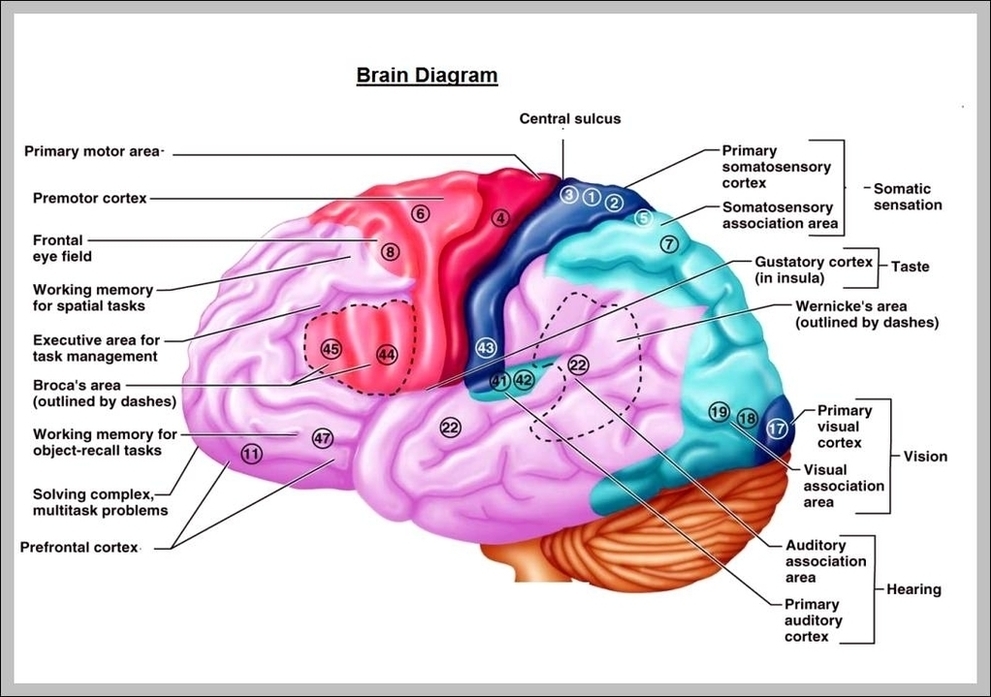
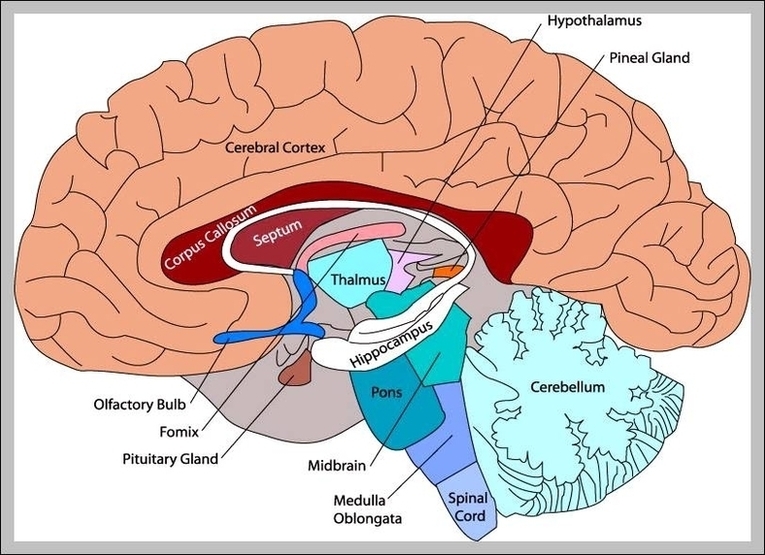
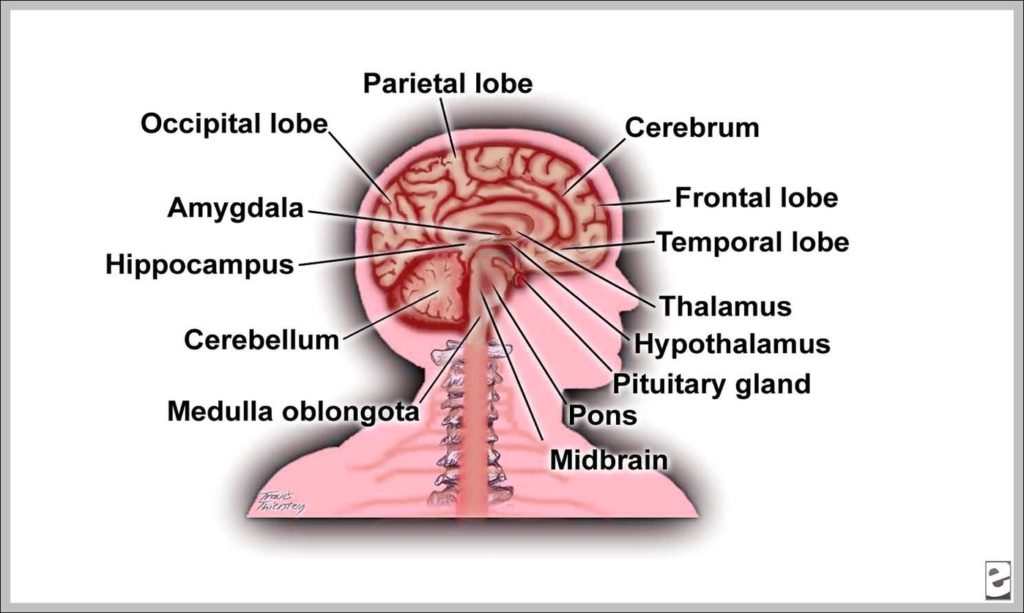
The human brain, a marvel of biological engineering, orchestrates our thoughts, emotions, memories, and bodily functions. Comprising approximately 3 pounds in the average adult, this intricate organ is about 60%…