Spinal Cord Anatomy
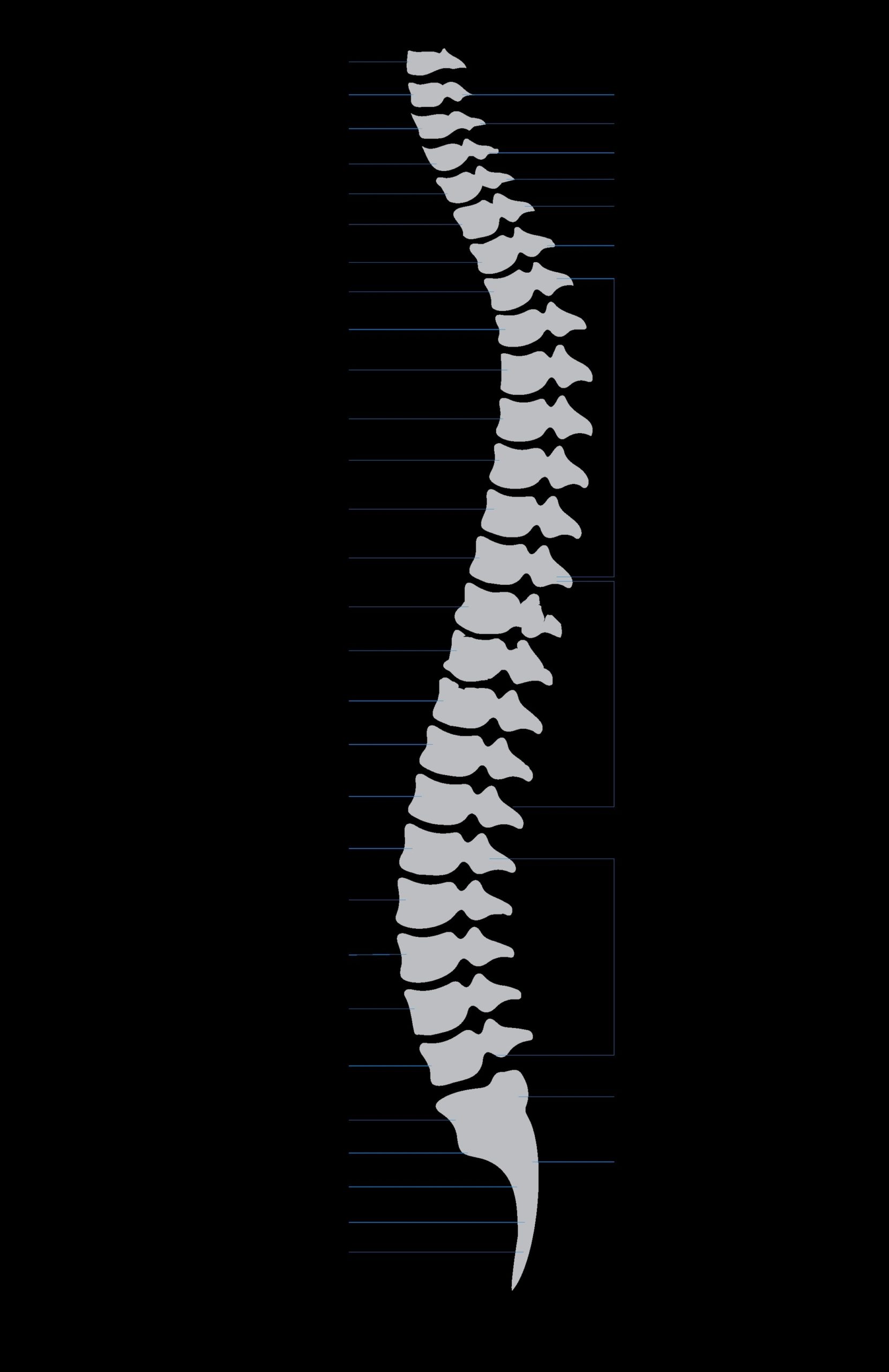
The spinal cord, a part of the central nervous system, is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue. It extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. The spinal cord is a continuation of the brainstem and extends from the foramen magnum at the base of the skull to the L1/L2 vertebra where it terminates as the conus medullaris.
The spinal cord is situated inside the vertebral canal of the vertebral column. In adults, the spinal cord occupies only the upper two-thirds of the vertebral canal. This is because the spinal cord finishes growing at the age of 4, while the vertebral column finishes growing at age 14-18.
The spinal cord is composed of an outer layer of white matter and centrally located gray matter. The gray matter is the dark, butterfly-shaped region of the spinal cord made up of nerve cell bodies. The white matter surrounds the gray matter in the spinal cord and contains cells coated in myelin, which makes nerve transmission occur more quickly.
The spinal cord comprises three parts: the cervical (neck), thoracic (chest), and lumbar (lower back) regions. Throughout its length, the spinal cord shows two well-defined enlargements to accommodate for innervation of the upper and lower limbs: one at the cervical level (upper limbs), and one at the lumbosacral level (lower limbs).
The spinal cord is protected by three layers of tissue: the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. These layers are collectively known as the meninges. The dura mater is the outermost layer, the arachnoid mater is the middle layer, and the pia mater directly covers the spinal cord.
The spinal cord functions include carrying signals between the brain and the rest of the body. It is essential for conducting impulses from the brain to the body and generating reflexes that make our daily functioning smooth.
The spinal cord is innervated by 31 pairs of nerves that emerge from the segments of the spinal cord to innervate the body structures. These include 8 pairs of cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal pair of spinal nerves.
In summary, the spinal cord is a crucial part of the central nervous system. It plays a vital role in transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body, enabling us to perform our daily activities smoothly. Its complex structure and function make it an essential component of our nervous system..