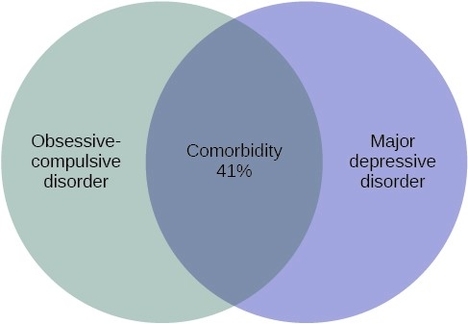
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental health disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities that were once pleasurable. This condition significantly impacts a person’s life, affecting their personal relationships, work performance, and overall quality of life.
ymptoms
The symptoms of MDD are pervasive and must last for at least two weeks for a diagnosis. They include:
– Persistent feelings of sadness or emptiness
– Feelings of hopelessness
– Irritability
– Loss of interest or pleasure in activities
– Fatigue or loss of energy
– Difficulty concentrating, remembering, or making decisions
– Changes in appetite or weight
– Sleep disorders
– Physical symptoms, such as headaches or digestive problems
Causes
The exact cause of MDD is often unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of several factors:
– Biological Factors: These include changes in neurotransmitter levels, altered brain function, and genetic predisposition.
– Psychological Factors: These encompass individual personality traits, early childhood trauma, and chronic stress.
– Environmental Factors: These involve adverse life experiences, such as loss or major life changes.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of MDD involves a comprehensive physical and mental health assessment. Blood tests may be performed to rule out other medical conditions that can cause similar symptoms. A psychological examination is conducted based on a questionnaire related to the symptoms and thoughts.
Treatment
Treatment for MDD typically involves a combination of medication and psychotherapy.
– Medication: Antidepressants such as Citalopram, Escitalopram, and Sertraline are often prescribed. These medications work by increasing the levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter known to control emotions.
– Psychotherapy: This involves talking about the condition and related issues with a mental health professional.
– Brain Stimulation Therapy: This includes treatments like Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS), which stimulates nerve cells in the brain involved in mood regulation and depression.
Prevention