Human Skeleton Anatomy
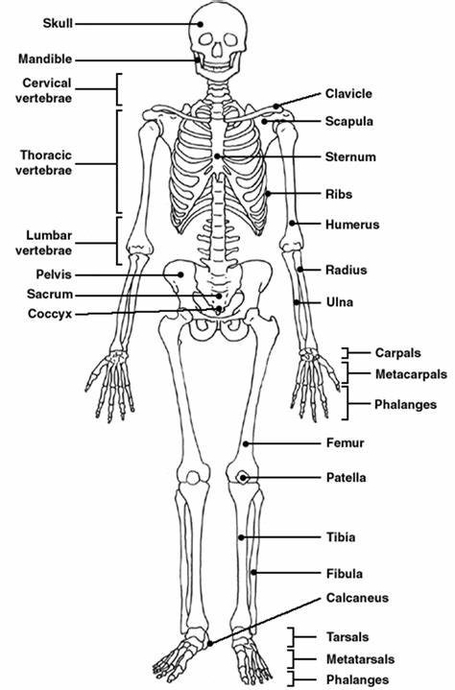
The human skeleton, an internal framework, serves as the backbone of the body, providing structure, protection, and enabling motion. It consists of 206 bones, cartilages, and bands of fibrous connective tissue the ligaments and tendons.
ubdivisions
The skeleton is divided into two main subdivisions:
1. Axial Skeleton: Comprises the vertebral column (spine), much of the skull, and the thoracic cage.
2. Appendicular Skeleton: Includes the pelvic (hip) and pectoral (shoulder) girdles and the bones and cartilages of the limbs.
Functions
The functions of the skeleton are threefold:
1. Support: The skeleton provides the main support for the body. The vertebral column, corresponding to the notochord in lower organisms, is the main support of the trunk.
2. Protection: The central nervous system lies largely within the axial skeleton, with the brain being well protected by the cranium and the spinal cord by the vertebral column.
3. Motion: The skeleton, in conjunction with the muscles and nerves, enables body movement.
Types of Bones
Bones of the human skeletal system are categorized by their shape and function into five types:
1. Long Bones: Example – Femur.
2. Flat Bones: Example – Frontal bone.
3. Sesamoid Bones: Example – Patella (knee cap).
4. Short Bones: Example – Carpals (in the hand) and tarsals (in the feet).
Additional Structures
The human skeleton also includes ligaments and cartilage. Ligaments are bands of dense and fibrous connective tissue that are key to the function of joints. Cartilage is more flexible than bone but stiffer than muscle. It helps give structure to the larynx and nose and is also found between the vertebrae and at the ends of bones like the femur.
In conclusion, the human skeleton is a complex and intricate system that plays a crucial role in body support, protection, and movement. Its understanding is fundamental to the fields of anatomy, physiology, and medicine..