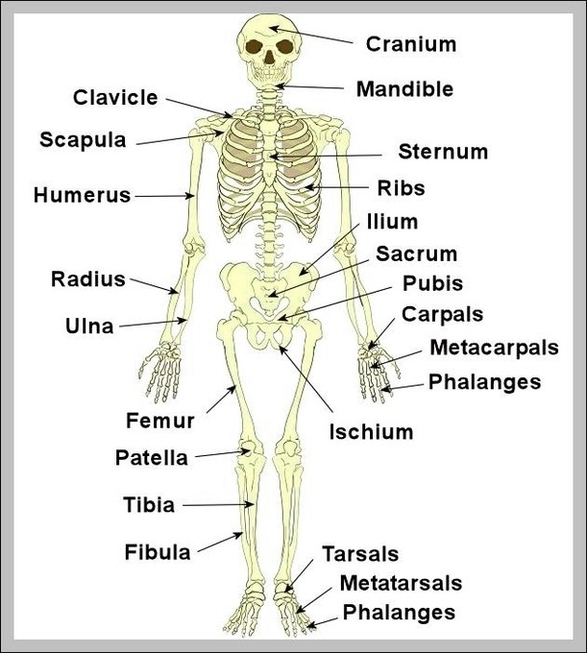
The Human Skeletal System
The human skeletal system is a complex structure that serves as the framework for the body, providing support, protection, and facilitating movement. It consists of bones, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments.
Components of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system can be divided into two main parts: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
1. Axial Skeleton: This consists of 80 bones forming the vertical axis of the body, including the bones of the head, neck, chest, and spine. Key components include:
– Skull: Comprises 22 bones, including eight cranial bones that protect the brain, and 14 facial bones.
– Auditory Ossicles: Six small bones within the inner ear canal, transmitting sound waves to the inner ear structures.
– Hyoid: A U-shaped bone at the base of the jaw, serving as an attachment point for neck muscles and ligaments.
– Vertebral Column: Made up of 26 bones, including 24 vertebrae, the sacrum, and coccyx (tailbone).
– Thoracic Cage: Comprises the sternum (breastbone) and 12 pairs of ribs, protecting the heart and lungs.
2. Appendicular Skeleton: This includes 126 bones that make up the arms and legs, as well as the bones that attach them to the axial skeleton.
Functions of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system performs three primary functions: support, protection, and motion.
1. Support: The skeleton provides the structural framework for the body, supporting soft tissues and providing attachment points for the tendons of most skeletal muscles.
2. Protection: The skeleton protects the body’s internal organs from injury. For example, the skull protects the brain, and the rib cage protects the heart and lungs.
3. Motion: Skeletal muscles are attached to bones; therefore, when the associated muscles contract, they cause bones to move.
Types of Bones
Bones are classified into five types: long bones, short bones, flat bones, sesamoid bones, and irregular bones.
Conclusion
The human skeletal system is a marvel of biological engineering, providing structural support, protecting vital organs, and facilitating movement. Understanding its intricacies helps us appreciate the complexity of our bodies and the importance of maintaining bone health.