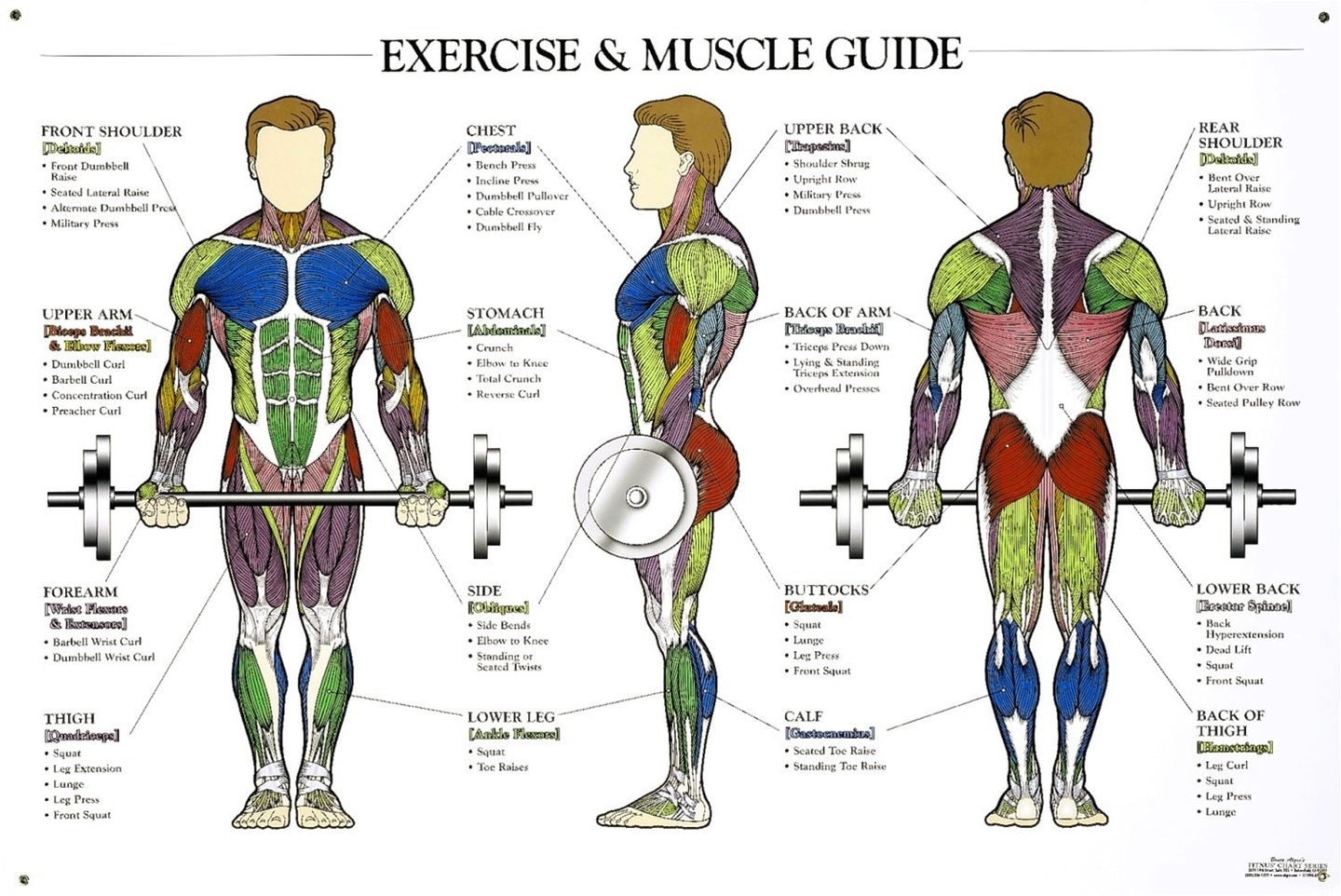
The human arm is a complex structure that enables a wide range of motion and functionality. It consists of numerous muscles that work in harmony to facilitate various movements. The arm muscles are broadly divided into two compartments: the upper arm and the forearm, each with its own set of muscles.
Upper Arm Muscles
The upper arm extends from the shoulder to the elbow and contains two compartments: the anterior and the posterior.
1. Anterior Compartment: This compartment is located in front of the humerus, the main bone of the upper arm. It includes:
– Biceps Brachii: This muscle has two heads that start at the front and back of the shoulder before joining together at the elbow. It helps with flexion and adduction of the upper arm.
– Brachialis: Located underneath the biceps, it acts as a bridge between the humerus and ulna, one of the main bones of the forearm. It’s involved with the flexing of the forearm.
– Coracobrachialis: Located near the shoulder, it allows adduction of the upper arm and flexion of the shoulder. It also helps to stabilize the humerus within the shoulder joint.
2. Posterior Compartment: This compartment is located behind the humerus and consists of two muscles:
– Triceps Brachii: This muscle runs along the humerus and allows for the flexion and extension of the forearm. It also helps to stabilize the shoulder joint.
– Anconeus: A small, triangular muscle that helps to extend the elbow and rotate the forearm.
Forearm Muscles
The forearm runs from the elbow to the wrist and contains more muscles than the upper arm. It contains both an anterior and posterior compartment.
1. Anterior Compartment: The muscles in this area are mostly involved with flexion of the wrist and fingers as well as rotation of the forearm.
2. Posterior Compartment: The muscles in this compartment are primarily involved in the extension of the wrist and fingers.
Each muscle in the arm plays a specific role in facilitating movement. They work together to allow you to perform all sorts of motions and tasks, from lifting heavy objects to delicate tasks that require fine motor skills. Understanding the anatomy and function of these muscles is crucial in fields like physiotherapy and sports science, where knowledge of the musculoskeletal system can help prevent injuries and improve performance.
In conclusion, the muscles of the human arm, with their intricate arrangement and specific functions, showcase the remarkable complexity and efficiency of the human body. They enable us to perform a wide array of tasks, making them an essential part of our daily lives.