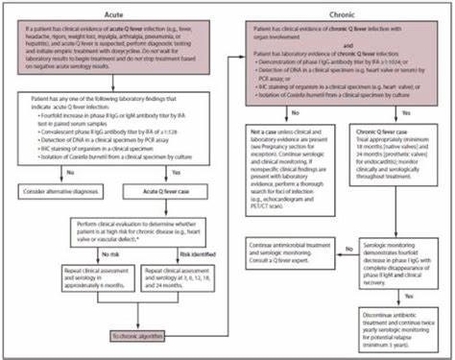
Understanding Heart Disease
Heart disease, also known as cardiovascular disease, is a term that encompasses a variety of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels. It is the leading cause of death in the United States and poses a significant health risk worldwide.
Types of Heart Disease
1. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): This is the most common type of heart disease, characterized by blockages in the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart. These blockages can lead to a decrease in blood flow to the heart muscle, depriving it of the oxygen it needs.
2. Heart Arrhythmias: Arrhythmias are conditions where the heart has an irregular beating pattern. Serious arrhythmias often develop from other heart problems but may also occur independently.
3. Heart Failure: In heart failure, the heart doesn’t pump blood as well as it should to meet the body’s needs. It is usually caused by coronary artery disease, but it can also occur due to thyroid disease, high blood pressure, heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathy), or certain other conditions.
4. Heart Valve Disease: The heart has four valves that open and close to direct blood flow between the heart’s four chambers, the lungs, and blood vessels. An abnormality could make it hard for a valve to open and close the right way, blocking your blood flow or causing blood to leak.
ymptoms of Heart Disease
The symptoms of heart disease can vary depending on the specific condition. However, common symptoms include chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, and pain in the neck, jaw, throat, upper belly area, or back. Other symptoms can include numbness, weakness, or coldness in the legs or arms if the blood vessels in those areas are narrowed.
Risk Factors
Certain factors may increase your risk of developing heart disease. These include age, physical inactivity, diabetes, family history of heart disease, high blood pressure, high levels of LDL “bad” cholesterol or low levels of HDL “good” cholesterol, obesity, smoking, and stress.
Prevention and Treatment
Prevention and management of heart disease often involve lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, avoiding tobacco, and managing stress. Medications may also be prescribed to control blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other contributing factors. In some cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to treat certain heart conditions.
Conclusion
Heart disease represents a significant global health challenge. Understanding its various forms, symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options is crucial for prevention and management. Despite its prevalence, many types of heart disease can be prevented and managed, underscoring the importance of awareness and proactive healthcare..