Antibiotics: Classes and Drug Names
Antibiotics are medications used to fight bacterial infections. They are one of the most highly utilized and important medication classes in medicine. Antibiotics are specific for the type of bacteria being treated and, in general, cannot be interchanged from one infection to another. They either kill the bacteria (bactericidal) or keep it from reproducing and growing (bacteriostatic). Antibiotics do not work against any viral infection.
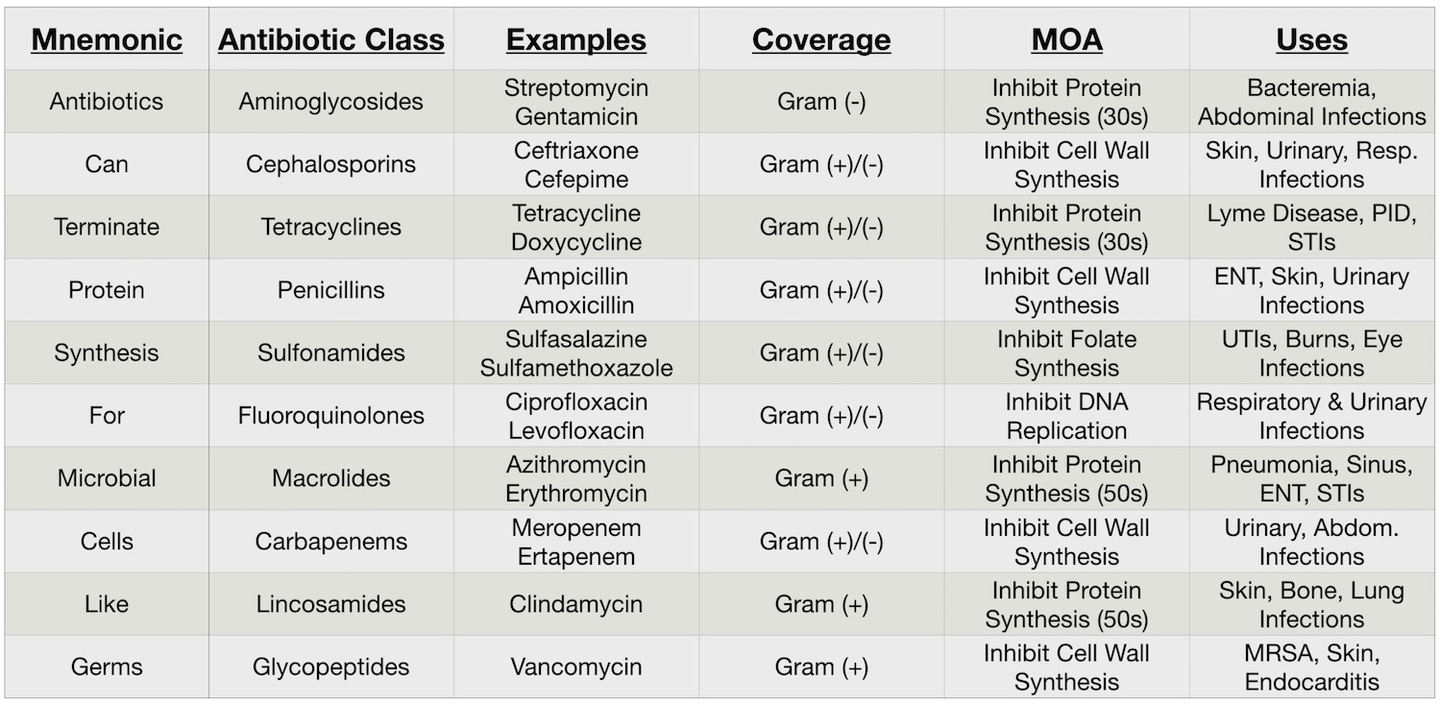
There are many different classes of antibiotics, each with its unique mechanism of action and conditions they treat. Here are some of the main classes of antibiotics:
1. Penicillins: This class includes drugs like penicillin and amoxicillin. They are used to treat a variety of infections, including strep throat and ear infections.
2. Cephalosporins: Drugs in this class include cephalexin. They are often used to treat infections like urinary tract infections.
3. Tetracyclines: This class is used to treat a variety of infections, including respiratory tract infections, acne, and certain sexually transmitted infections.
4. Macrolides: This class includes drugs like erythromycin and azithromycin. They are often used to treat respiratory tract infections and skin infections.
5. Fluoroquinolones: This class includes drugs like ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin. They are used to treat a variety of infections, including urinary tract infections and respiratory tract infections.
6. Aminoglycosides: This class includes drugs like gentamicin and tobramycin. They are often used to treat severe infections caused by gram-negative bacteria.
7. Sulfonamides: This class includes drugs like sulfamethoxazole. They are often used to treat urinary tract infections and ear infections.
8. Carbapenems: This class includes drugs like meropenem. They are used to treat severe or high-risk bacterial infections.
9. Lincosamides: This class includes drugs like clindamycin. They are used to treat serious infections caused by anaerobic bacteria.
10. Glycopeptides: This class includes drugs like vancomycin. They are used to treat serious, multi-drug resistant infections.
Each class of antibiotics has a unique mechanism of action, meaning they target bacteria in different ways. Some inhibit the synthesis of bacterial cell walls, while others inhibit protein synthesis or DNA replication within the bacterial cell. This diversity allows for the treatment of a wide range of bacterial infections.
It’s important to note that antibiotics should be used responsibly to avoid antibiotic resistance. This occurs when bacteria change in response to the use of antibiotics and become resistant to the drug that was once able to kill them. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are harder to kill and can cause infections that are more difficult to treat..